As technology continues to evolve, the way that PCB assembly is manufactured has also transformed. From the hand-soldering of components in the past to fully automated manufacturing today, advancements have enabled faster production with greater accuracy and precision. This article will explore how this evolution has taken place over time and what it means for PCB assembly going forward.
1. Overview of PCB Assembly History
The history of PCB assembly is an interesting one, stretching back to the 1950s when engineers first began soldering components by hand. Since then, significant advances have been made in technology that allows for more efficient and automated production methods.
With the advent of surface mount technology (SMT) in the 1980s, manufacturers were able to produce circuit boards with smaller parts and greater efficiency than ever before. Major advancements such as automated wave soldering machines and pick-and-place robots have further increased manufacturing speed while maintaining high-quality standards. Today’s PCB assembly processes are highly advanced thanks to years of development which has allowed for faster turnaround times on complex projects without compromising precision or reliability.
2. Hand-Soldering Era: Pre-Automation Challenges and Solutions

The hand-soldering era of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly presented a unique set of challenges and solutions. With the lack of automated equipment, workers were required to manually assemble components on PCBs using physical tools. This labor-intensive process was time-consuming and prone to errors, leading to lower-quality products with higher costs than today’s standards.
To combat these issues, manufacturers had to develop creative methods for both improving worker efficiency and reducing the amount of human error in their operations. One solution manufacturers used was shifting from simple manual soldering processes towards more advanced techniques such as wave soldering or reflow ovens which heated components at a much faster rate than manual soldering irons could achieve. Automated pick-and-place machines also began emerging around this time which allowed for quicker component placement onto PCBs than humans could manage with traditional methods.
Finally, technological advances like X-ray inspection systems helped reduce the risk of faulty connections by allowing workers to detect potential defects before they caused further problems down the line. Through a combination of improved production techniques and enhanced technology, companies were able to create efficient processes capable of meeting consumer demands while maintaining high levels of product quality despite the lack of automated manufacturing capabilities during this period in history.
3. Introduction to Automated Manufacturing Technologies
The introduction of automated manufacturing technologies into the PCB assembly process has revolutionized the way boards are assembled. Automated processes provide unprecedented accuracy, efficiency, and reliability in production, allowing for faster turnaround times and higher-quality products than ever before.
From pick-and-place machines to reflow ovens, these technologies have been instrumental in modernizing PCB assembly. In this section, we will explore how automated technologies can be used to streamline production from start to finish. We’ll look at the various components that come together to make up a completely automated system, as well as how these systems can be integrated with other processes such as testing or inspection. Finally, we’ll discuss some of the challenges associated with implementing an automated solution and what steps can be taken to mitigate them.
4. Benefits of Automating the PCB Assembly Process
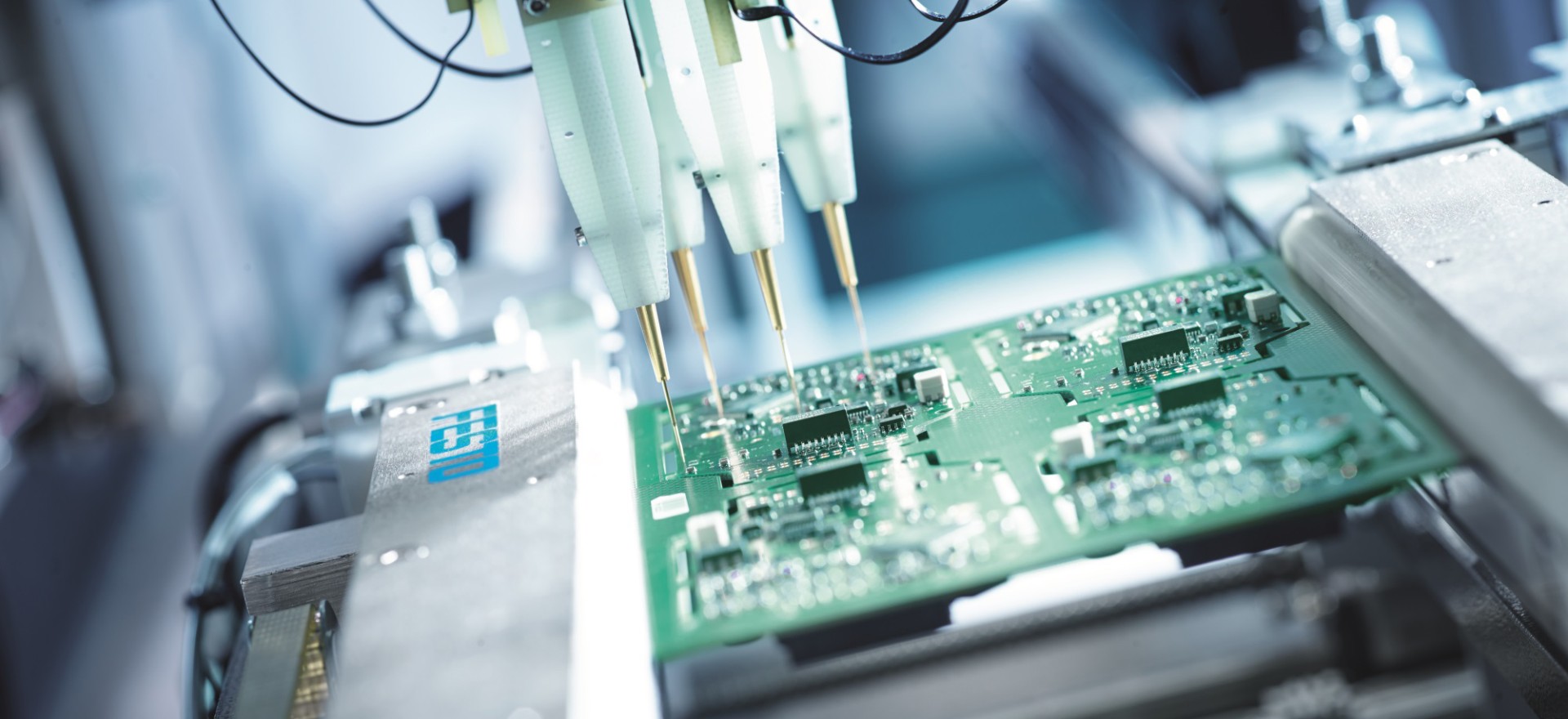
The automated PCB assembly process offers a variety of benefits to manufacturers. Automation streamlines the entire production line, significantly reducing labor costs and time-to-market. Additionally, it eliminates potential human errors associated with manual soldering and enables greater precision in component placement thanks to its repeatable accuracy.
Furthermore, automated processes are more energy efficient than traditional hand-soldering techniques, which can help reduce operational costs over time. Finally, automation allows for higher volumes of production and improved quality assurance when compared to manual soldering methods. With these advantages in mind, it is clear that automating the PCB assembly process brings tremendous benefits to modern manufacturing operations.
5. Future Trends in PCB Manufacturing
The future of PCB assembly is brighter than ever. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for automated manufacturing will only be further explored. Robotics and AI are being used more and more in production lines, allowing for greater efficiency and accuracy with fewer human errors.
Automated optical inspection systems can detect even the smallest of defects before they become an issue, ensuring quality assurance every step of the way. With increased automation also comes to a decrease in costs over time as labor, materials, and energy all become optimized through technological progress.
Additionally, 5G networks are helping to facilitate smarter communication between machines on the factory floor, leading to faster processing times while still maintaining data security standards. The combination of all these advancements have sparked an exciting revolution in PCB assembly that promises great potential for years to come!